Many studies have shown that biodiversity regulates multiple ecological functions that are needed to maintain the productivity of a variety of ecosystem types. What is unknown is how human activities may alter the ‘multifunctionality’ of ecosystems through both direct impacts on ecosystems and indirect effects mediated by the loss of multifaceted biodiversity. Using an extensive database of 72 lakes spanning four large Neotropical wetlands in Brazil, we demonstrate that species richness and functional diversity across multiple larger (fish and macrophytes) and smaller (microcrustaceans, rotifers, protists and phytoplankton) groups of aquatic organisms are positively associated with ecosystem multifunctionality.
Research and publish the best content.
Get Started for FREE
Sign up with Facebook Sign up with X
I don't have a Facebook or a X account
Already have an account: Login
Revue de presse et du net par le Pôle de partage des connaissances S&T de l'Office français de la biodiversité
Curated by
DocBiodiv
 Your new post is loading... Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading... Your new post is loading...
|




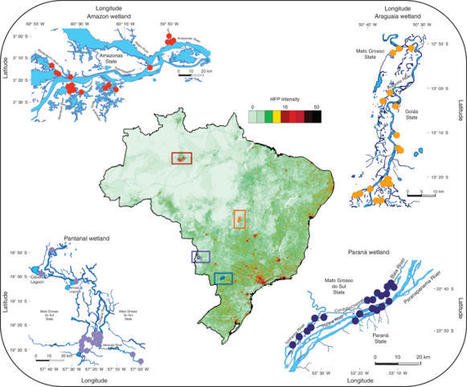



Moi, D.A., Lansac-Tôha, F.M., Romero, G.Q. et al. Human pressure drives biodiversity–multifunctionality relationships in large Neotropical wetlands. Nat Ecol Evol (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-022-01827-7