Depuis plus de 50 ans, les écologues se questionnent sur les causes derrière la stabilité des écosystèmes. Est-elle le fruit de l’interaction entre une grande variété d’espèces, comme l’indiquent les théories les plus anciennes ? Ou bien, peut-elle être à l’origine de bouleversements et d’extinctions d’espèces ? Ian Hatton, chercheur associé au Département des sciences de la terre et des planètes de l’Université McGill, apporte des éléments de réponse dans une récente étude.
Get Started for FREE
Sign up with Facebook Sign up with X
I don't have a Facebook or a X account
 Your new post is loading... Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading... Your new post is loading...

Agrodoc Ouest's curator insight,
April 20, 2020 3:55 AM
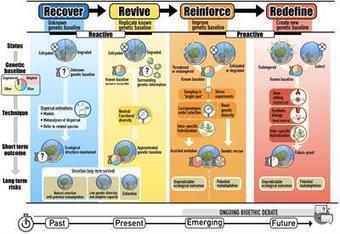
La détérioration globale des habitats des écosystèmes marins a conduit à la nécessité d'interventions actives pour stopper ou inverser la perte de la fonction écologique. La restauration a toujours été un outil essentiel pour inverser la perte d'habitats et restaurer les fonctions, mais on ne sait pas dans quelle mesure cela sera suffisant sous les climats futurs. Les technologies génétiques émergentes permettent aujourd'hui de restaurer de manière proactive l'adaptabilité des espèces cibles aux conditions environnementales futures prévues, ce qui ouvre la possibilité de renforcer la résistance aux stress futurs dans les habitats dégradés et menacés. Ainsi, le choix de restaurer les bases historiques ou d'anticiper l'avenir reste une décision clé qui influencera le succès de la restauration face au changement environnemental et climatique. Nous présentons ici un aperçu des différentes motivations de la restauration - récupérer ou faire revivre les habitats perdus ou dégradés dans leur état actuel ou historique, ou renforcer ou redéfinir les conditions futures. Nous nous concentrons sur les choix génétiques et adaptatifs qui sous-tendent chaque option et sur les conséquences qui en découlent pour la réussite de la restauration. Ces options couvrent un éventail de trajectoires possibles, d'avancées technologiques et d'acceptabilité sociétale, et représentent un cadre pour faire progresser la restauration des espèces formant des habitats marins dans le futur.
|
|










Le Devoir, Pascaline David, Collaboration spéciale, 20 avril 2024
Diversity begets stability: Sublinear growth and competitive coexistence across ecosystems. March 2024. Science 383(6688):eadg8488 DOI:10.1126/science.adg8488