Anthropogenic light is ubiquitous in areas where humans are present and is showing a progressive increase worldwide. This has far-reaching consequences for most species and their ecosystems. The effects of anthropogenic light on natural ecosystems are highly variable and complex. Many species suffer from adverse effects and often respond in a highly specific manner. Ostensibly surveyable effects such as attraction and deterrence become complicated because these can depend on the type of behavior and specific locations. Here, we considered how solutions and new technologies could reduce the adverse effects of anthropogenic light.
Research and publish the best content.
Get Started for FREE
Sign up with Facebook Sign up with X
I don't have a Facebook or a X account
Already have an account: Login
Revue de presse et du net par le Pôle de partage des connaissances S&T de l'Office français de la biodiversité
Curated by
DocBiodiv
 Your new post is loading... Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading... Your new post is loading...
|
|






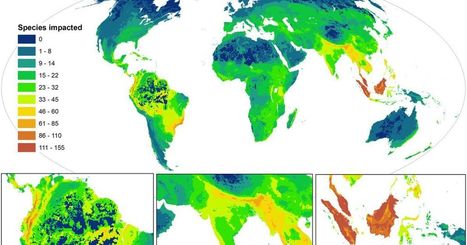




Annika K. Jägerbrand, Kamiel Spoelstra .Science 380, 1125-1130 (2023) .DOI:10.1126/science.adg3173
Dans l'actualité scientifique "pollution lumineuse", voir aussi :
- Léa Mariton. Taking light pollution effects on biodiversity into account in conservation measures : challenges and prospects. Case study of European bat species. Biodiversity and Ecology. Sorbonne
Université, 2023. HAL Id: tel-04042599 https://theses.hal.science/tel-04042
- via @ulrikacandolin "Happy to announce a forthcoming review on impact of Light Pollution on aquatic invertebrates, in Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology"
- via @Airam_Rguez Moonlight diminishes seabird attraction to artificial light Airam Rodríguez, Elizabeth Atchoi, Beneharo Rodríguez, Tania Pipa, Matthieu Le Corre, David G. Ainley 01 Sept2023